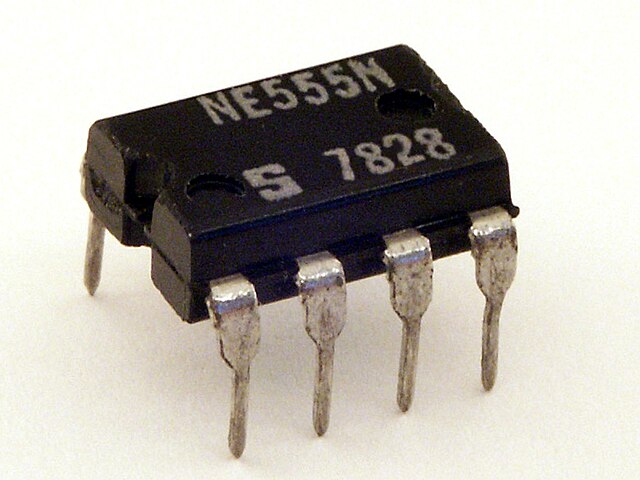
555 Timer IC NE555 LM555 Timer IC
First introduced by Signetics in the early 1970s, the NE555 timer remains a foundational component in electronics due to its reliability, simplicity, and broad tolerance to supply voltage and temperature. The LM555 from National Semiconductor offers enhanced comparator stability via current‑mirror active loads and altered comparator priority logic to reduce timing drift over temperature.
Both chips are available in DIP‑8, SOIC‑8, or VSSOP packages and are pin‑identical, allowing seamless replacement in most designs.
🛠 Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (VCC) | 4.5 V – 15 V (up to 18 V abs. max) |
| Output Drive | ±200 mA source/sink |
| Timing Range | Microseconds to hours (RC-dependent) |
| Operating Modes | Astable, Monostable, Bistable, Schmitt |
| Logic Family | Bipolar TTL |
| Comparator Thresholds | ~1/3 VCC trigger, ~2/3 VCC threshold |
| Propagation Delay | ~2 µs typical |
| Package Types | DIP‑8, SOIC‑8, VSSOP-8 |
| Operating Temperature | 0°C to 70°C (commercial grade) |
💡 Use Cases & Applications
-
⚙️ Astable Clock Source: Produces square waves to drive LEDs, counters, or generate PWM signals without a microcontroller.
-
⏱ Monostable One‑Shot Timers: Generate precise delays for push‑buttons, sensors, or reset circuits.
-
🔁 Latch/Bistable Mode: Debounce switches or create simple flip‑flop logic.
-
🧠 Analog Signal Conditioning: Shape noisy inputs into clean digital pulses via Schmitt‑trigger behavior.
-
📡 Tone/Audio Generation: Produce audio frequencies for alarms, buzzers, or signal playback.
⏳ NE555 vs LM555 — What’s the Real Difference?
Both ICs are largely interchangeable, but subtle internal modifications make them behave slightly differently under edge conditions:
-
LM555 uses current‑mirror active loads in its comparator design, improving stability with less timing drift across temperature and voltage changes.
-
The trigger vs threshold priority is reversed compared to the NE555, so LM555 may suppress unwanted pulses in overlapping trigger-threshold conditions, whereas NE555 triggers immediately on a trigger even if threshold is high.
-
For most DIY or hobby circuits—even in precision timing—the NE555 remains popular and lower cost, with slightly higher dependence on supply and temperature.
🛠️ Pair With
-
⚡ Use with Power Supplies for stable input voltage
-
🧩 Combine with Electronic Components like timing resistors, capacitors, and signal buffers
-
🧰 Test and assemble with Tools & Accessories such as breadboards or oscilloscopes
🎥 YouTube Tutorial
⚠️ Precautions & Tips
-
Always place a 0.1 µF bypass capacitor between VCC and GND to avoid supply noise affecting timing.
-
Base your pulse calculations using the standard formula: t_high = 0.693 (Rₐ + R_b) × C, t_low = 0.693 R_b × C.
-
Be mindful: LM555 may behave differently under simultaneous threshold/trigger signals. Test in your specific circuit if overlapping events are possible.
-
Ensure all floating inputs are held stable (e.g., RESET tied high).
🏁 Summary & CTA
The NE555 and LM555 remain among the most enduring and flexible ICs in electronics—timers that design engineers and hobbyists rely on year after year. Whether for generating clocks, timing delays, or creating latch logic, their dependability and simplicity make them indispensable components.
🛒 Available now at Electroway — get your classic timer ICs with trusted quality and fast delivery.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.